Ephion Health Validates a New System to Monitor the Status of Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy Patients

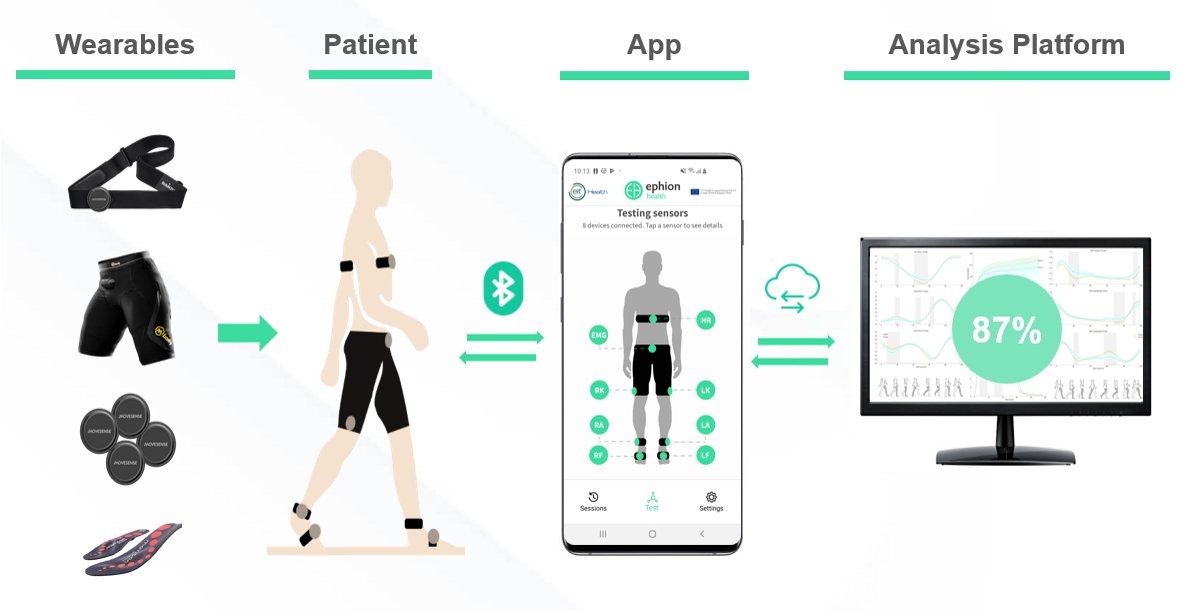
The Spanish health tech company Ephion Health recently published a monitoring system to measure gait biomechanics in Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy (DMD) patients using wearable sensors. The system integrates eight commercial wearables. It consists of five Movesense Medical sensors for inertial measurement, one of which also measures heart rate, two plantar pressure insoles from Moticon and electromyography shorts from Myontec. All sensors are connected to Ephion Mobility app that collects data from all sensors simultaneously.
In the development project, researchers calculated more than 100 biomechanical and physiological parameters from the sensor data. These include several spatio-temporal parameters, joint angles, heart rate evaluation, muscle activation and vertical force. From the wide range of parameters, Ephion Health developed an AI-Score that uses all the repeatable and relevant parameters to measure disease progression in DMD ambulant patients.
A clinical study with the title “Multidimensional Biomechanics-Based Score to Assess Disease Progression in Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy”, validating the AI-Score against the current standards, was published in Sensors in January. The AI-Score called 6M+ and 2M+ demonstrated not only high accuracy and stability, but also a higher correlation with age, suggesting that the AI-Score better characterizes gait regressions in DMD than currently used assessment methods. Read the free full-text article.
Versatile use of Movesense sensors
The research team used Movesense MD sensors in the project in different ways that made great use of the sensor’s versatility. One of the areas was the calculation of joint angles (trunk, hip, knee and ankle) during gait by combining inertial data from sensors attached to consecutive segments (chest, thigh, shank and foot (insoles)). Movesense data was also combined with data from plantar pressure inertial sensors to calculate ankle flexion.
Additionally, Movesense sensors were used to compute some spatio-temporal parameters, such as gait velocity, step length, and step time. The team also used the sensor data to identify certain events, for example turns during the walking test, to automatically record the walking distance. Finally, a chest-mounted heart rate sensor was used to monitor effort during the test.
Ephion Mobility app uses the SDKs of Movesense, Moticon and Myontec to connect and collect data from the different sensors simultaneously. The app uses time stamps to synchronize data from different sensors.
Currently, Ephion Health is using the system developed in the project to target other patient populations, such as different neuropathies and other neuromuscular diseases. The company has also started a collaboration project with private hospital group Quiron Salud to quantify the risk of falling of frail elderly patients, both in the hospital and remotely.
Through all these pilots, new parameters can be calculated, such as joint angles in three directions of rotation (flexion, abduction and internal rotation). In the future, it is also planned to calculate inverse dynamics by combining Movesense data and plantar pressure data.
To learn more about the project, watch a video Ephion Health, the digital platform to measure patient health and predict medical outcomes on YouTube. Find more information about the company, its products and services on Ephion Health website.
To evaluate Movesense Medical sensor for your needs, download a spec sheet. To test the sensor in practice, get a developer kit and start experimenting! Movesense team is always available for further discussions to help you get started and support your project.
Views: 183
